Dynamic contact angles provide information about contact angle hysteresis, which originates from the properties that differ from the ideal surface. Therefore, dynamic contact angle measurement can indicate chemical and topographical heterogeneity. The advancing and receding values dynamic contact angles are extremes of the possible contact angle range.
What is Dynamic Contact Angle?
A contact angle is defined by intersect of the three phase boundary between liquid, solid and vapor, and it is often described by Young’s equation,
γsv = γsl + γlv cos θ
Young’s equation only applies to ideal solids with smooth, inert, homogeneous and nonporous surfaces. However, surface roughness and chemical heterogeneity is often present on real surfaces, and as a result the accurate determination of contact angles is challenging as surface irregularities can cause contact angle hysteresis. The static contact angle is normally defined as the average value of various contact angle measurements. However, this can lead to great errors due to the irregularity of the real surface. The dynamic contact angles are the extremes of a possible contact angle range and they occur when the three-phase boundary is in motion. Dynamic contact angles provide information on the topography and homogeneity of the surface.
Dynamic contact angles can be measured with several® Attension tensiometers.
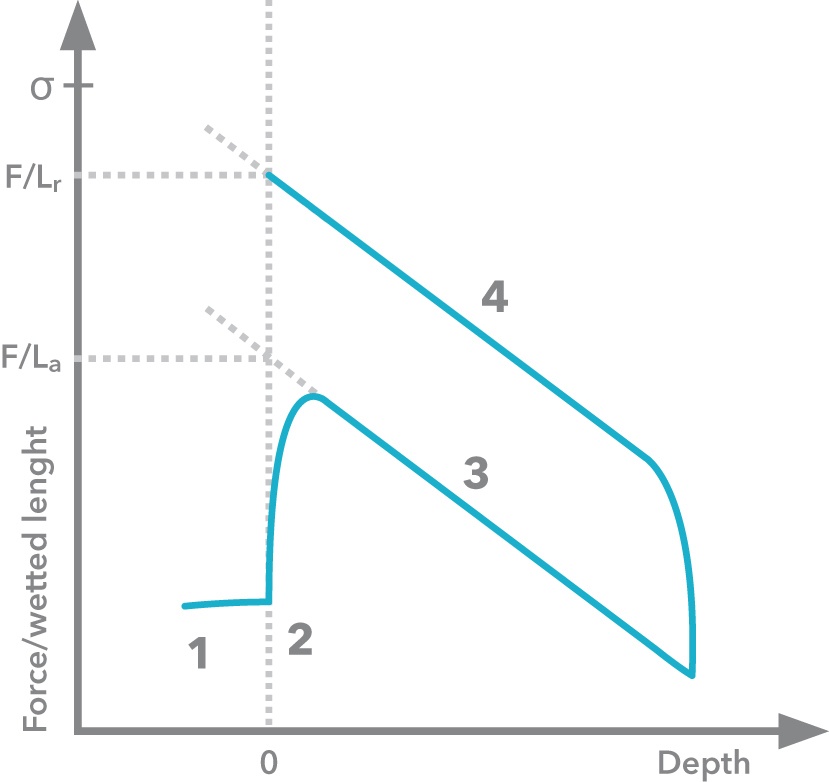
With the Attension Sigma force tensiometer, the Wilhelmy method can be used to define dynamic contact angles. The solid surface is attached to a balance hook and is immersed in a test liquid to calculate the advancing contact angle. The solid is then lifted from the test liquid and the receding angle can be calculated.
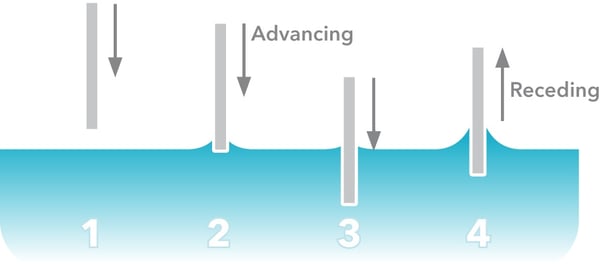
There are two methods for measuring dynamic contact angles with the Attension Theta optical tensiometer. The first one is done by expanding (advancing contact angle) and decreasing (receding contact angle) the drop size with the dispenser.
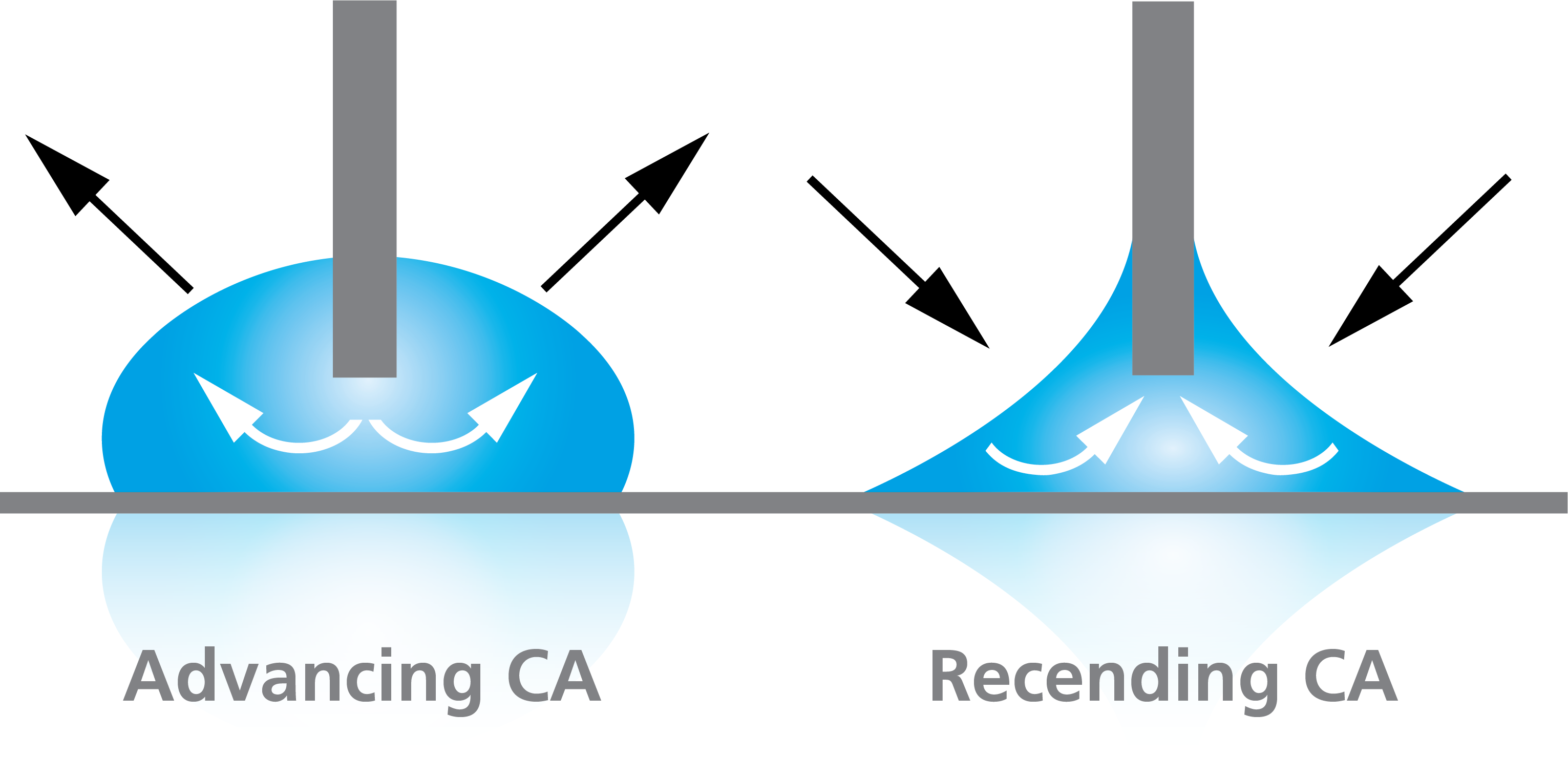 The other method is done by tilting either the sample stage or the whole instrument with the tilting cradle. By doing that, at some point the droplet will start to move. The advancing angle is then measured at the front edge of the droplet and the receding angle from the back of the droplet. Tilting cradle can be also used for measuring the roll off angle of the surface. The roll off angle refers to the inclination angle of a solid surface in which a droplet rolls off the surface.
The other method is done by tilting either the sample stage or the whole instrument with the tilting cradle. By doing that, at some point the droplet will start to move. The advancing angle is then measured at the front edge of the droplet and the receding angle from the back of the droplet. Tilting cradle can be also used for measuring the roll off angle of the surface. The roll off angle refers to the inclination angle of a solid surface in which a droplet rolls off the surface.
To read how the tilting plate method and roll-off angle has been utilized in coating development, please download the case study below.

Our tensiometer selector guides you to your optimal instrument.
Try the instrument selector
