- Products
- QSense
- QCM-D Instruments
- QSense Analyzer
QCM-D
QSense Analyzer
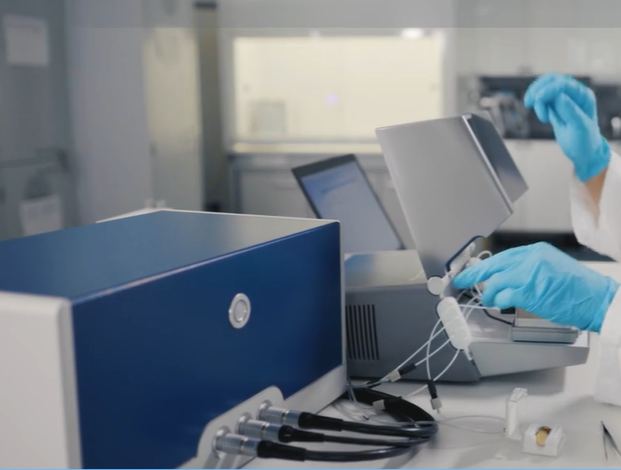
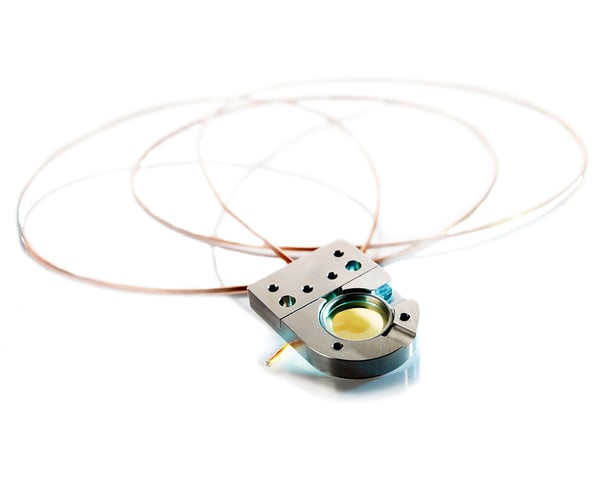
Both flexible and time-saving, QSense Analyzer enables you to study molecular interactions at surfaces and interfaces in real-time, running up to four measurements in parallel.
phenomena
-
Adsorption
-
Desorption
-
Binding and interactions
-
Swelling
-
De-swelling, crosslinking and collapse
-
Degradation, corrosion and etching
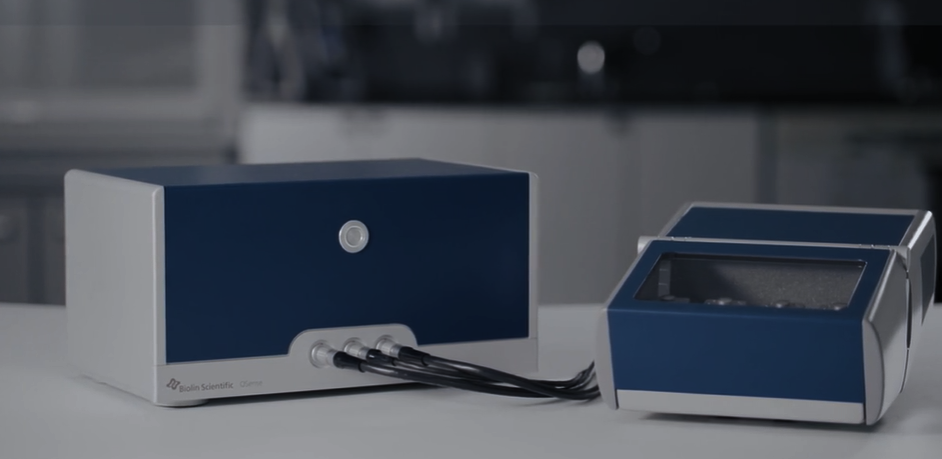

Versatility and parallel measurements
Key features
-
Measure mass, thickness, and viscoelastic properties of rigid and soft films
7-harmonic QCM-D with QSense Decay technology enables qualitative and quantitative analysis -
Flexibility of manual procedures
Full freedom to interact during measurements and easy to change between different experimental setups. -
4 measurement channels
Enable the evaluation of different substrates and/or samples in parallel and simplify data comparison -
Versatile
Allows for several experimental combinations and set-ups, directly or via add-on chamber -
Modular and flexible
Easy to add-on capabilities and switch between different modules -
Broadest offer of sensor surfaces and coatings
Set up model systems that are as close as possible to real-world conditions
QSOFT AND DFIND SOFTWARE
%20(1).gif?width=900&name=analyzer%20(1)%20(1).gif)
QSense software is tailored to help you maximize the potential of your QCM-D measurements. With QSoft capturing your data and Dfind simplifying your analysis, you can streamline your research process effortlessly.
measurement conditions
-
Flow mode
-
Stagnant mode
-
Liquid phase
-
Gas phase Requires add-on.
-
Harsh chemicals
-
Low temperature Requires add-on
-
High temperature Requires add-on
-
Humidity Requires add-on
-
Variable pressure Requires add-on
-
Inert surface Requires add-on
Measurement range and capacity
| Measurement channels | 4 |
| Working temperature | 15 to 65 °C, 4 to 150 °C using accessory chamber (QSense High Temperature chamber) |
| Sensors (frequency range) | 5 MHz (1-72) |
| Number of measured harmonics |
7, allows for full viscoelastic modeling |
Sample and fluidics
| Minimum sample volume, stagnant mode | ~ 40 μl ~ 10 μl using add-on module (QSense Open module) |
| Minimum sample volume, flow mode | ~ 200 μl |
| Flow rates | 25-150 μl/min applicable for QSense setup (Peristaltic pump settable to 0-1 ml/min) |
Performance characteristics
| Maximum time resolution* | 300 datapoints per second (each datapoint represents an f and D value) |
| LOD (3 x noise) | 1.34 ng/cm2 |
| Sensitivity/limit of detection and noise | See the graph below |
| Minimum noise |
Frequency: 0.03 Hz Mass: 0.5 ng/cm2 Dissipation: 12∙10-9 |
| Long-term stability** | Frequency: < 1 Hz/h Dissipation: < 0.15∙10-6 Temperature: < 0.02˚C/h |
* Maximum time resolution applying one measurement channel.
** The temperature stability depends on variations in how the ambient affects the warming or cooling of the chamber. The specified temperature stability may not be reached if the room temperature changes more than ± 1° C, if there is a draft or a heat source nearby.
All specifications are subject to change without notice.
Article
Optimal real-life performance
Applying a higher sample rate inevitably leads to higher noise and thus a compromised limit of detection (LOD). What aspect to prioritize depends on the studied surface interaction process. High time resolution may not be critical if very slow changes are studied, and a high measurement sensitivity may not be important if large changes are to be measured. With the 5 Speed-to-Noise modes you can select the right setting to maximize real-life performance for your measurement.
The figure and table below describe the real-measurement performance of QSense Analyzer for each acquisition mode. This is much more interesting than maximum values in a specification to understand what to expect from your instrument in a real measurement situation.
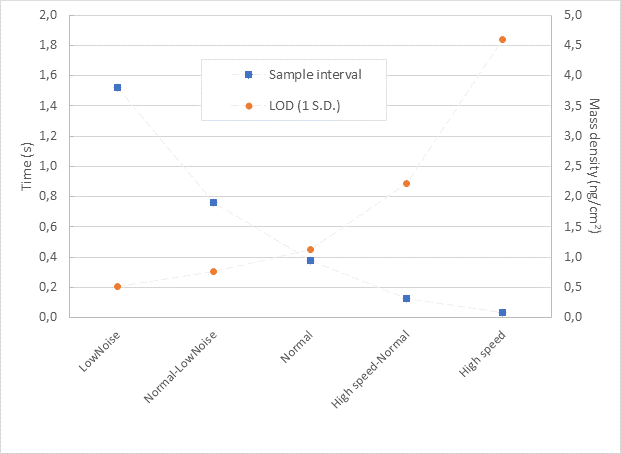
Speed and limit of detection (LOD) per acquisition mode. Limit of detection is set to 1 S.D. of the baseline noise.
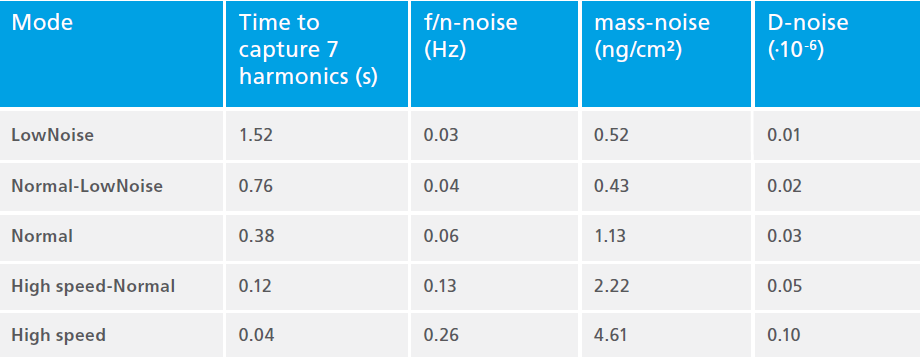
Performance characteristics. Measurements were performed with QSX 303 SiO2 sensors at 20°C temperature, and in deionized water at a flow of 15µL/min, using one measurement channel. Each measurement mode was measured for approximately 5 minutes. Note that using more than one channel will reduce the measurement time resolution.
QSoft and Dfind software
QSense softwares are designed for you to make the most out of your QCM-D measurements. QSoft is collecting your data whereas Dfind makes your analysis easier.
Dfind features
- A complete analysis toolbox
One software for all your needs - Intuitive interface
Dfind supports you all the way through your analysis process - from data preparation to final reporting - Guided modelling
To take you through your analysis step by step - Material library
Configuring your modelling setup is easy, just select your sample material from the list - Autoplotting
Visualizes your results throughout the whole analysis - Smart tools
Dfind offers several analysis methods including shifts, rates and slopes to help you extract the information you need - Analyze all data in one go
To save your time, Dfind allows you to review, model and analyze multiple data sets in one go
Computer requirements
Required
- PC with 64-bit Windows 7 SP1, 8, 8.1 or 10
- At least 1366×768 px screen resolution
- At least 4 GB RAM
Recommended
- 1920×1080 Full HD screen resolution.
- At least 8 GB RAM
- At least 50 GB HD space
- Core i5 5th generation Intel (or comparable) processor or better
Add more possibilities
Explore the extras for QSense Analyzer that will extend your measurement context.
High Temperature Chamber
With the High Temperature Chamber you can perform measurements in an extended temperature range of 4-150°C.
Humidity Module
This module is designed to enable measurements of vapor uptake and release from thin films coated on the sensor.
PTFE Flow Module
Flow Module with an interior coating of PTFE. Suitable for measurements sensitive to titanium which is the interior material of the standard flow module.
ALD Holder
ALD is short for Atomic Layer Deposition. This module is designed for measurements in vacuum or gas phase.
What others say
Our instruments are present at many prestigious universities and research facilities worldwide. Take a minute to find out what others say about QSense.

Sivashankar Krishnamoorthy on QSense
"We use the QSense Explorer and Analyzer systems. We could get started rather quickly, thanks to the ease of using the systems."

Dr Sivashankar Krishnamoorthy, Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology
"We spent time to understand different ways to customize the sensor chips, assay configuration, and flow routines to rational design of nanoplasmonic and nanopatterned sensors. Have had a great experience so far."

Marité Cárdenas on QSense
"QSense instruments are a great tool for our biophysical research. They enable rapid screening for biomolecular interaction at lipid bilayers and also allow optimizing the parameters for deposition of thin films."

Professor Dr. Marité Cárdenas, Health and Society, Malmö University
"The instrument is easy to use, and has a long working life as long as you follow the maintenance instructions! The technical staff at Biolin Scientific are a pleasure to work with: They are nice and always give quick feedback and support."

Kenichi Sakai on QSense
"We regard QCM-D as a valuable measuring tool due to its high sensitivity and stability and find it applicable for versatile studies because of its availabilities of sensors with different types of surfaces. In this context I would say QCM-D is the best suitable solution for simulating a variety of nanoscale interaction behaviors both real-time & in-situ.

Kenichi Sakai, Associate Professor, Tokyo University of Science
"We are working on academic research in the field of colloid and interface chemistry and our main work is synthesis of novel surfactants and characterization of their properties. We use QCM-D as a must-tool to comprehend molecular adsorption/desorption behaviors specifically observed at a solid-liquid interface."

Jodie Lutkenhaus on QSense
"We can monitor the mass change of our system in real-time. I can tell you that for every electron moved, this amount of mass changed. That’s powerful. You can’t really get that with any other system."

Jodie Lutkenhaus, Associate Professor, Texas A&M University
"We use the QSense high temperature model that allows us to investigate polyelectrolyte complexes and their response to temperature. We’re also using the electrochemistry module so we can run our standard electrochemical measurements at the same time as we run the QCM-D."

Malkiat Johal on QSense
"I have found QSense to be one of the best techniques for an undergraduate lab because it’s turnkey and it requires very little maintenance."

Malkiat Johal, Professor of Chemistry, Pomona College
"The operating principles are straightforward and the students can focus on the science. And so, that’s something that we have been really happy with, it really works in this kind of setting. It’s an ideal method for an undergraduate surface science lab."
Learn more
We have gathered all our in-depth knowledge associated with QSense Analyzer. Browse around amongst guides, overviews and white papers to find a topic of interest.
- QSense
How Excipients, Surfaces and Formulation Conditions Affect Therapeutic Proteins
- QSense

Basics of QCM-D
- QSense

How to Optimize the QCM-D Baseline Stability
- QSense

The Working Principles of QCM and QCM-D
- QSense
QCM-D in Drug Formulation and Storage
- QSense

QCM-D vs SPR
- QSense

QCM-D vs other QCMs
- QSense

What is Piezoelectricity?
- QSense

How QCM Results are Influenced by Layer Distribution
- QSense

Why the Resonance Frequency of a QCM Sensor is 5MHz
- QSense

Characterization of Polymer-based Systems
- QSense

Using QCM-D in the Food Industry
- QSense
What is Biocompatibility?
- QSense

Why it is Useful to use Multiple Overtones in QCM Measurements?
- QSense

Nanocellulose Research with QCM-D
- QSense
Analysis of Surfactant-Surface Interactions with QSense
- QSense

Getting Started with QSense Dfind
- QSense

Data Modeling in QSense Dfind
- QSense

QCM-D as a Screening Tool for Protein Adsorption
- QSense

Analyzing Vapor Uptake and Release with QCM-D
- QSense
Surface Science – a Field Rich in Science and Applications
- QSense

QCM-D Data Analysis
- QSense
QCM-D as a Tool to Study the Binding of Viruses
- QSense

Key Publications on the Formation of Supported Lipid Bilayers
- QSense

Characterization of Surfaces and Surface Reactions in Energy Storage
- QSense
Development of a New Method for the Formation of SLBs on Solid Support using QSense QCM-D
- QSense

QSense Etching Guide
- QSense
QCM-D Characterization of Antimicrobial Lipid Interactions with Supported Lipid Bilayers: Towards Antiviral Applications in the Biomedical and Agricultural Sectors
- QSense

Monitoring of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Build-up and Crosslinking using QCM-D
- QSense
Biomembrane Models and Interactions Therein
- QSense

Screening Nanoparticle - Protein Interactions
- QSense
The Sauerbrey Relation
- QSense

QSense Cleaning Profile
- QSense

QCM-D Studies of Engineered Nanoparticles
- QSense
Analytical Methods to Characterize Lipid-based Systems
- QSense
Characterization of Biomolecular Interactions
- QSense

QCM-D and Neutron Reflectometry
- QSense
QCM-D Analysis in Virus-related Research
- QSense

Determining Cleansing Efficacy of Elfan AT 84 using a QCM-D Assay
- QSense

Analyze Surface-induced Complement Activation
- QSense
Adsorption and Aggregation of Monoclonal Antibodies at Silicone Oil-Water Interfaces
- QSense
How do we Stop the Next Pandemic from an Unknown Virus?
- QSense

Characterization of Polymer Layer Swelling, Crosslinking and Collapse
- QSense

Analyzing Cleaning of Hard Surfaces with QSense
- QSense
QSense Analysis in CMP
- QSense

The Dissipation Factor in QCM-D Technology
- QSense

Temperature Stability in QCM Measurements
- QSense

What is Dissipation?
- QSense

What is a Viscoelastic material?
- QSense

How to Generate Quality QCM-D Data
- QSense

QCM-D vs other QCMs
- QSense

QCM-D Publications in Battery Research
- QSense

How to read a QCM Specification
- QSense
Dfind Basic Training Course
- QSense

Information Obtained with QSense QCM-D
- QSense
How to Characterize Lipid-Based Systems with QCM-D
- QSense

QCM-D in Research
- QSense