
Biomedical devices are at the forefront of modern healthcare, playing crucial roles in diagnostics, treatment, and patient care. From catheters and implants to stents and diagnostic tools, these devices often require specialized surface coatings to ensure optimal performance, safety, and longevity. But how do we know if a coating will adhere well and perform as intended? One powerful technique for evaluating coatings is contact angle measurement—a simple yet insightful method for probing surface properties and adhesion.
Coatings on biomedical devices serve multiple purposes. They can enhance biocompatibility, reduce friction, prevent bacterial adhesion, or deliver therapeutic agents. Common coatings include hydrophilic layers to improve wettability, hydrophobic barriers to repel fluids, and antimicrobial films to reduce infection risks. However, the effectiveness of these coatings depends not only on their chemical composition but also on their ability to adhere strongly to the underlying device and maintain their properties in challenging biological environments.
For example, a hydrophilic coating on a catheter can reduce patient discomfort and lower the risk of infection, but only if it remains intact and firmly attached throughout use. Similarly, drug-eluting coatings on stents must adhere reliably to ensure controlled drug release and device safety.
Strong adhesion between a coating and its substrate is essential for device reliability. Poor adhesion can lead to delamination, where the coating peels away, potentially causing device failure or adverse biological reactions. Factors influencing adhesion include the surface chemistry and roughness of the device, the compatibility of coating materials, and the methods used for surface preparation.
Ensuring robust adhesion is especially challenging in biomedical applications, where devices may be exposed to bodily fluids, mechanical stress, and sterilization processes. Therefore, evaluating and optimizing adhesion is a key step in the development and quality control of coated biomedical devices.
Contact angle measurement is a widely used technique for characterizing surface wettability and energy. It involves placing a droplet of liquid (typically water) on a surface and measuring the angle formed between the droplet’s edge and the surface. This angle provides valuable information about how the surface interacts with liquids:
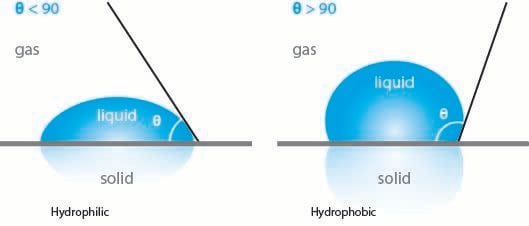
There are several methods for measuring contact angle, including the sessile drop technique (placing a static droplet on the surface) and dynamic methods (measuring advancing and receding angles as the droplet volume changes).
Contact angle measurements can indirectly reveal information about coating adhesion. Surface energy, which is closely related to contact angle, plays a significant role in determining how well a coating will adhere to a substrate. Generally, a substrate with higher surface energy (lower contact angle) promotes better adhesion of coatings.
By measuring the contact angle before and after surface treatments (such as plasma cleaning or chemical modification), researchers can assess whether the treatment has increased the surface energy and thus the potential for strong adhesion. Consistent, reproducible contact angles after coating application also suggest uniform coverage and good adhesion.
For instance, if a hydrophilic coating is applied to a device and the measured contact angle drops significantly compared to the uncoated surface, this indicates successful modification. If the contact angle increases over time or after exposure to stress, it may signal coating degradation or delamination.
Beyond adhesion, contact angle measurements are valuable for evaluating other coating properties:
These insights are critical for ensuring that biomedical devices meet stringent performance and safety standards.
To obtain reliable contact angle data, careful sample preparation and standardized measurement protocols are essential. Surfaces should be clean and free of contaminants, and measurements should be repeated at multiple locations to assess uniformity. It’s also important to interpret contact angle results in the context of the specific biomedical application—what constitutes an “ideal” contact angle may vary depending on the desired device function.
While contact angle measurement is a powerful tool, it is often complemented by other analytical techniques, such as surface energy calculations, microscopy, and mechanical adhesion tests, to provide a comprehensive picture of coating performance.
Coatings are vital to the function and safety of biomedical devices, and their performance hinges on strong adhesion and well-defined surface properties. Contact angle measurement offers a fast, non-destructive, and informative way to assess both adhesion and the functional characteristics of coatings. As biomedical technology advances, integrating surface science techniques like contact angle analysis will be key to developing next-generation devices that are safer, more effective, and longer-lasting.
Learn about the effect of surface roughness and wettability on biocompatibility of biomaterials and medical devices.
Contact angle measurements offer insight into the behavior of a biomedical device in the human body.
Sign upp for the webinar to learn more about how QCM-D is used to study biomaterial-induced activation of the immune system
The concept of wettability, its importance in biomaterials, and how it can be manipulated to improve biocompatibility and overall performance are reviewed.
Read about how QSense QCM-D analysis is used in the quest to tackle inflammation and bacterial infections on implant surfaces.
Learn about the past and future development of biomaterials in regenerative medicine.
Learn about the distinction between the two concepts biomaterials and tissue engineering and how they relate to each other.
Learn more about how biocompatibility is defined and what this property entails
