There are many processes all around us, both naturally occurring and artificially designed, where thin films or coatings degrade or breakdown and material desorb. A typical example would be etching or corrosion, which in, for example, pipeline infrastructure, is an unwanted process, but which in manufacturing of electronic components is highly desired. Another area where film degradation is highly desired, is in soil removal by detergent. In both cases, it is important to understand the material degradation so that it can be optimized and controlled. Either to be able to prevent the unwanted degradation, or to increase the speed of the wanted one. To be able to control the process, it must be mapped out and understood. It can therefore be relevant to monitor both the degradation rate as well as the extent of the degradation. QCM-D, which essentially is a balance for small masses, can measure and quantify this film degradation. Both in terms of amount as well as the kinetics.
When a thin film degrades, there will be mass lost from the surface. There will also be a decrease in thickness of the initial surface-bound layer. These are two parameters that QCM-D measures in real-time at nanoscale resolution.
As an example, let’s have a look at film degradation when cleaning a surface. We have a fat stain that we would like to remove from the surface using a surfactant. As outlined in Figure 1, we follow the steps below.
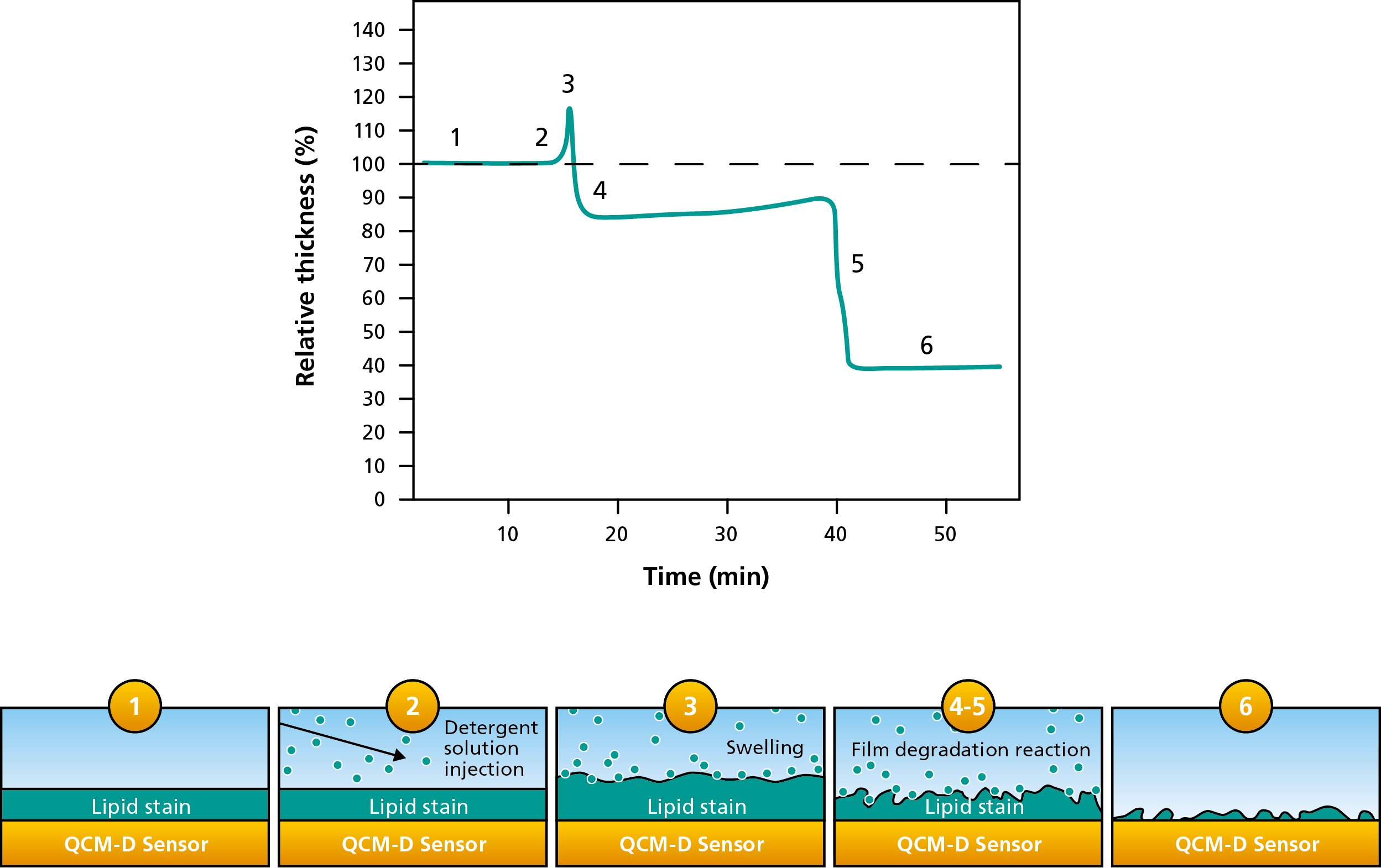
Figure 1. Monitoring a cleaning process with QCM-D technology.
Monitoring the mass and thickness as a function of time, one can easily characterize and evaluate the degradation behavior and amount of material removed. It is also possible to compare the behavior under different conditions, such as by varying chemical concentration, temperature, and pH.
In addition to these two examples, other types of degradation that could be characterized by measuring the mass loss include, for example, enzymatic reactions, dissolution, light-induced degradation as well as temperature-induced degradation.
Download the application note to read the full study:
Learn how QSense QCM-D reveals protein–surface interactions and adds interface-focused insight to biopharmaceutical formulation and stability work
Learn how QSense sensors enable application‑relevant biointerface interaction analysis and explore our sensor offering for different areas
Learn how QSense QCM D can be used to analyze swelling of thin films, including magnitude and dynamics.
Read about how molecule-surface interaction processes such as adsorption and desorption can be analyzed with QCM-D.
Learn best practices and step-by-step methods for accurate QCM-D coating thickness measurement on QSense sensors using QSense Omni.
Compared to QCM, QCM-D measures an additional parameter, and provides more information about the system under study.
Discover how QCM-D analysis reveals real-time etching dynamics, helping optimize cleaning processes and protect surfaces from unwanted damage.
Discover how QSense QCM-D helps tackle fouling challenges across industries
Discover how QCM-D enables real-time, label-free analysis of supported lipid membrane formation, structure, and dynamics for advanced research
Learn how QSense QCM-D analysis can reveal membrane fouling dynamics and optimize cleaning strategies for more efficient water treatment
Learn how QSense QCM-D helps detect and prevent surface-induced instabilities in biologics. Join our webinar for insights and practical examples.
