
Developing high-performance cleaning products requires more than just knowing what’s left behind after cleaning. To truly optimize formulations and protocols, it’s essential to understand how cleaning happens—moment by moment—under realistic conditions. Traditional “before-and-after” tests can’t deliver this level of insight, often leaving knowledge gaps that can slow down development and innovation. QCM-D (Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation monitoring) is a surface-sensitive technology that can help fill in these missing pieces, offering real-time, detailed information on the cleaning process as it unfolds.
QCM-D is a surface-sensitive, time resolved analysis technology that measures mass changes and viscoelastic properties on surface-adhering layers at the nanoscale. For cleaning product developers, this means you can follow how soils are being removed from a surface, see how quickly the cleaning happens, and quantify how much residue remains after rinsing—all in a single experiment.
To demonstrate how QCM-D works and its ability to reveal cleaning process dynamics, we performed a technical study where industry-soiled surfaces were reproduced by applying heat-treated corn oil to stainless steel. We then compared the efficiency of three different eco-surfactants—A, B, and C, all designed for low-temperature oil removal and recovery—in removing the oil across a temperature range of 15–55°C.
With QCM-D, we monitored:
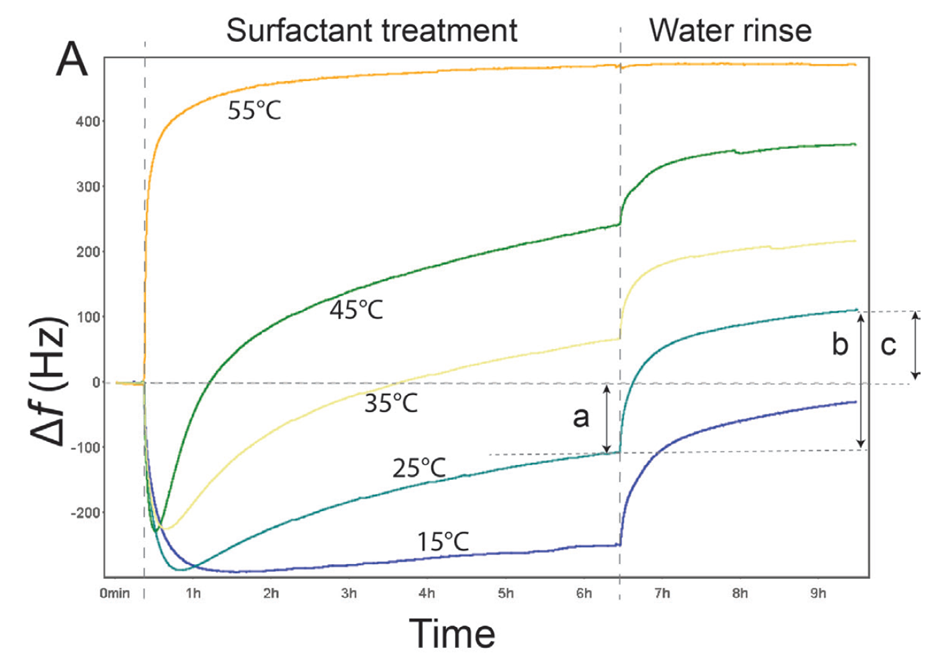
Figure 1. Temperature Dependence of Soil Removal Using QCM-D. This graph shows how much corn oil is removed from a sensor surface by surfactant A at five different temperatures (15°C, 25°C, 35°C, 45°C, and 55°C), measured in real time with QCM-D. The curves track the cleaning process over time. The arrows highlight key points at 25°C: a: Amount of soil removed after 6 hours of surfactant treatment (before rinsing). b: Additional soil removed during the rinse step. c: Total soil removed after both cleaning and rinsing steps. This real-time data helps product developers see exactly how cleaning performance changes with temperature and process steps.
The QCM-D measurements revealed how the three surfactants interacted with the soil at the five different temperatures. Looking, for example, at the measurement of surfactant A, Fig. 1, at 15°C, upon surfactant exposure, there is initially a decrease in Δf, indicating mass uptake, followed by a slow increase in Δf, indicating mass loss. In the rinse step, there is a sharp increase in Δf, indicating that mass is leaving the surface during the rinse. Comparing the results from the five different temperatures for surfactant A, it is noted that the behavior is similar to that observed at 15°C, but the magnitude of the shifts is temperature dependent. The data shows that both the removal rate and the total soil removal are temperature dependent for this surfactant and increase with increasing temperature.
To highlight the main trends, we are here presenting a single example dataset. The full study, including comprehensive results and analysis, is available in the technical white paper.
A comparison of the data for surfactants A, B, and C revealed the following key findings:
If you are looking to boost the efficiency of your cleaning products and streamline your development workflow, QCM-D can provide detailed, mechanistic insights beyond what traditional before-and-after methods offer. Whether you are benchmarking new surfactants or fine-tuning complex formulations, QCM-D enables data-driven decisions that can help reach superior cleaning results.
Interested in the full study and practical applications of QCM-D in cleaning analysis? Download the technical white paper below to explore the details.
Discover how QCM-D analysis reveals real-time etching dynamics, helping optimize cleaning processes and protect surfaces from unwanted damage.
Learn how QSense QCM-D analysis can reveal membrane fouling dynamics and optimize cleaning strategies for more efficient water treatment
Explore QSense QCM-D sensors to optimize cleaning efficiency with real-time insights, enhancing formulations and protocols across various conditions.
Discover how QSense QCM-D technology reveals real-time cleaning insights. Join our webinar to enhance your cleaning strategies and efficiency.
QSense QCM-D technology enables analysis of cleaning process dynamics, surface etching, and surface residual
Cleaning product performance assessments can be time-consuming, but with the right approach, evaluation and ranking can take less than one hour.
Read about the different components in cleaning products and how they work on a molecular level.
Soil removal efficiency of a formulation is typically assessed by running a cleaning test followed by an analysis of the result. Here we show how these two steps can be run simultaneously.
Yousra is an Application Scientist at Biolin Scientific. She has a strong interdisciplinary research background and deep technical expertise in laboratory technologies, with a particular focus on surface science instruments. Holding a Ph.D. in Biology and Biochemistry, Yousra has extensive experience in diverse fields, including biomaterials, microbiology, and surface chemistry.
