
Membrane fouling is a persistent challenge in water treatment, reducing efficiency and increasing operational costs. In this post, we demonstrate how Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) analysis can help address this issue by providing detailed insights into fouling dynamics and cleaning strategies.
Membrane fouling remains a significant challenge in modern water treatment processes, particularly as global demand for clean water rises and freshwater sources decline. Technologies such as wastewater treatment and seawater desalination increasingly rely on membrane filtration, but the accumulation of foulants—especially algal-derived organic matter (AOM) like sodium alginate—can severely degrade membrane performance. Even with pretreatment steps like microfiltration (MF) and ultrafiltration (UF), fouling persists, leading to reduced efficiency, higher maintenance costs, and operational disruptions. Understanding the dynamics of fouling and developing effective cleaning strategies are therefore essential for optimizing water treatment operations.
QCM-D is a surface-sensitive, time-resolved technology that enables label-free analysis of molecular interactions at surfaces and interfaces. By monitoring changes in resonance frequency (Δf) and dissipation (ΔD) of a quartz crystal sensor, QCM-D can characterize and quantify processes at the solid-liquid interface. Specifically, Δf provides information about mass changes at the surface, while ΔD indicates the softness or thickness of the layer.
In this case study, QSense QCM-D was employed to investigate how fouling layers form and respond to cleaning on membrane surfaces, with a focus on the structural and mechanical properties of the fouling layer. The study aimed to:
A bare gold QCM sensor was coated with a thin polyethersulfone (PES) layer to mimic the surface properties of a UF membrane. The experiment was designed to represent the inside of membrane pores, enabling the study of molecular interactions. The following solutions were used:
The sequence of solution injections was: NaCl, alginate, NaCl, cleaning agent (NaOH or Deconex), and a final NaCl rinse. All experiments were conducted at 25°C with a flow rate of 20 μL/min using the QSense Omni instrument.
The QCM-D data, Fig. 1, revealed several key findings:
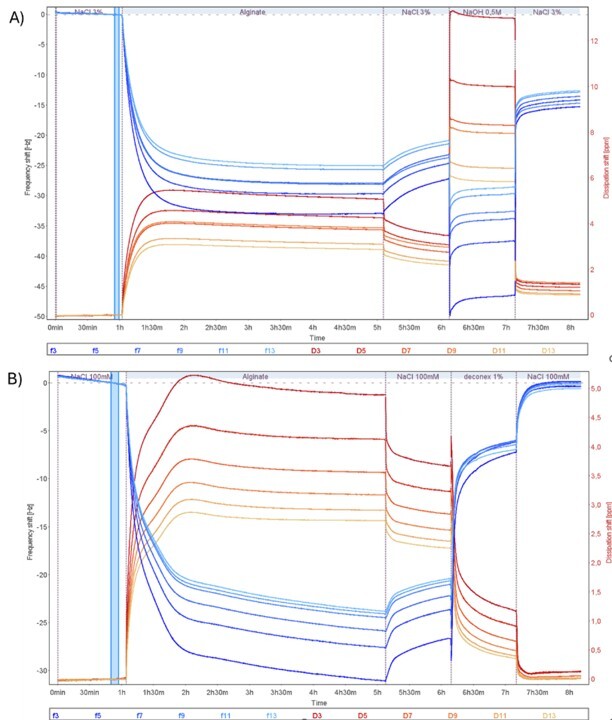
Figure 1. QCM-D raw data (Δf and ΔD) showing the time-resolved interaction of alginate with a PES membrane and subsequent fouling removal using NaOH (plot A) and 1% Deconex (plot B).
Comparative analysis showed that both cleaning agents reduced alginate fouling, but with different efficiencies:
Mechanistic insights from the acoustic ratio (ΔD/Δf) indicated that NaOH primarily removed softer, loosely bound components, leaving behind a more rigid residual layer. In contrast, Deconex was more effective at removing the entire fouling layer, resulting in a softer, cleaner surface.
This case study demonstrates the value of QSense QCM-D for real-time, sensitive monitoring of membrane fouling and cleaning. The technology provided critical insights into both mass changes and viscoelastic properties of fouling layers, enabling direct comparison of cleaning strategies. The described method can serve as a starting point for investigating different filter materials, surface modifications, types of fouling, and cleaning protocols, ultimately supporting the development of more efficient water treatment processes.
To learn more and to explore detailed results, download the full case study
Learn how QSense QCM-D reveals protein–surface interactions and adds interface-focused insight to biopharmaceutical formulation and stability work
Learn how QSense sensors enable application‑relevant biointerface interaction analysis and explore our sensor offering for different areas
Learn how QSense QCM D can be used to analyze swelling of thin films, including magnitude and dynamics.
Read about how molecule-surface interaction processes such as adsorption and desorption can be analyzed with QCM-D.
Learn best practices and step-by-step methods for accurate QCM-D coating thickness measurement on QSense sensors using QSense Omni.
Compared to QCM, QCM-D measures an additional parameter, and provides more information about the system under study.
Discover how QCM-D analysis reveals real-time etching dynamics, helping optimize cleaning processes and protect surfaces from unwanted damage.
Discover how QSense QCM-D helps tackle fouling challenges across industries
Discover how QCM-D enables real-time, label-free analysis of supported lipid membrane formation, structure, and dynamics for advanced research
Yousra is an Application Scientist at Biolin Scientific. She has a strong interdisciplinary research background and deep technical expertise in laboratory technologies, with a particular focus on surface science instruments. Holding a Ph.D. in Biology and Biochemistry, Yousra has extensive experience in diverse fields, including biomaterials, microbiology, and surface chemistry.
