
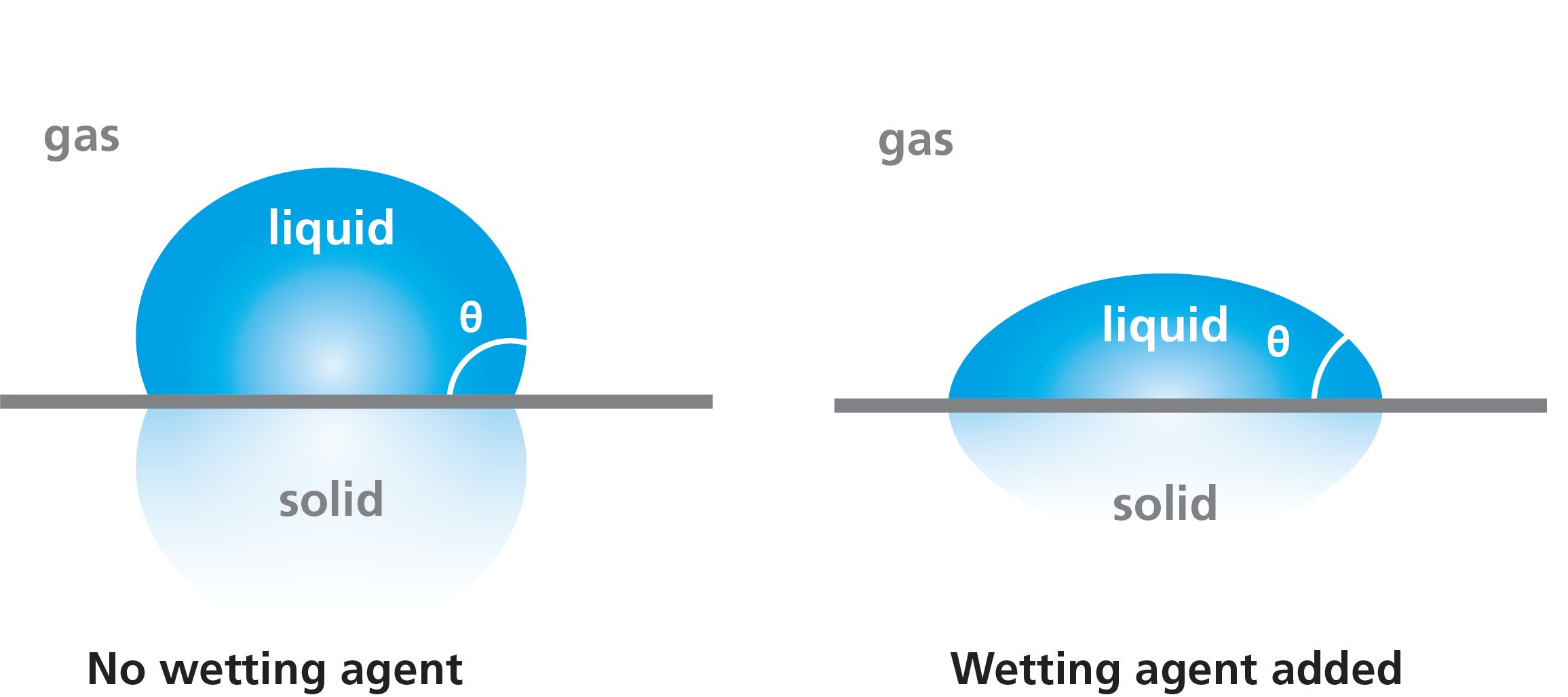
Wetting agents are surface-active molecules, or surfactants, specifically designed to reduce the surface tension of water. High surface tension can pose significant challenges in various applications where the spreading and penetration of water are crucial. These applications span across industries, including paints and coatings, detergents, pesticides, and more.
The primary function of a wetting agent is to lower the surface tension of water, which is naturally high at 72.8 mN/m (at 20 °C). This high surface tension can hinder the effectiveness of water-based solutions in industrial processes, as it prevents the solution from adequately wetting the surfaces it is applied to. By reducing surface tension, wetting agents enable these solutions to spread more effectively.
Coating Industry: In the coating industry, wetting agents play a crucial role in the pigment dispersion process. They help the fluid phase to wet pigment particles, ensuring a uniform application. Additionally, they reduce the surface tension of the coating, allowing it to properly adhere to the substrate.
Pesticides: Wetting agents enhance the efficiency of pesticides by facilitating the spread of the solution on leaf surfaces. This is particularly important for overcoming the waxy surfaces of many insects, fungi, and plants, which can otherwise resist penetration by water-based solutions.
Detergents and Cleaning Products: In detergents, wetting agents help water to spread and penetrate surfaces more effectively, improving cleaning performance by breaking down oils and dirt.
Wetting agents belong to the broader class of surfactants. These molecules are surface-active, meaning they tend to adsorb at air-liquid or liquid-liquid interfaces. By inserting themselves between water molecules, surfactants reduce the cohesive forces among them, thereby lowering surface tension.

To ensure optimal performance, the efficiency of wetting agents is often evaluated through surface tension measurements. These measurements not only indicate how effectively a wetting agent reduces surface tension but also help determine the appropriate amount needed for specific applications. Accurate surface tension measurement is critical for optimizing the use of wetting agents in industrial processes.
For more detailed insights into surface tension and its measurement methods, please download our comprehensive white paper through the link below.
The term surfactant comes from the word surface active agent. At the interface, they align themselves so that the hydrophobic part is in the air and the hydrophilic part is in water. This will cause a decrease in surface or interfacial tensions.
Surface tension plays an important role in Li-ion battery slurry optimization.
Surface tension plays an important role in the electroplating solution.
When measuring contact angles or making surface tension measurements with a pendant drop, selecting the correct tip or needle for your liquid is crucial.
The surface tension of water is about 72 mN/m at room temperature which is one of the highest surface tension for liquid.
Surface tension is a quantitative measure that can be correlated with a solution’s ability to remove dirt.
Surface tension and wettability are important physical properties that play a significant role in the effectiveness of agrochemicals.
Explains three different methods to measure surface tension.
