
Analysis of adsorption of biomolecules to solid surfaces is relevant in many areas, for example in biomedical engineering and in pharmaceutics, to name a few. Here we show how QSense QCM-D can be used to characterize biomolecular adsorption and desorption dynamics, as well as the amount adsorbed or desorbed from the surface of interest.
There are many situations where biomolecules are interacting with surfaces and where the biomolecular adsorption can have a great impact. One example, is when a medical implant is introduced into a body. In this situation, adsorption of biomolecules to the surface is a first step towards successful integration of the implant. Another example, where biomolecular adsorption, on the contrary, is undesired, is in the marine industry. Surfaces in subsea environment are exposed to a range of marine organisms. This may result in undesired biomolecular adsorption, and even colonization of some organisms.
In both of these cases, it is relevant to characterize and understand the biomolecular interaction with, and adsorption to, the solid surface of interest so that the surface properties and condition can be optimized to achieve, or prevent, biomolecular adsorption. One tool that can be used for biomolecular adsorption analysis is QSense QCM-D.
QSense QCM-D is a surface sensitive technology for label-free analysis of surface interactions and binding. Monitoring changes of mass at the surface as a function of time, it allows you to monitor biomolecular adsorption and desorption to solid surfaces, Fig 1. The time-resolved data also makes it possible to quantify how fast the adsorption/desorption is and how much material that adsorbs to, or desorbs from, the surface.
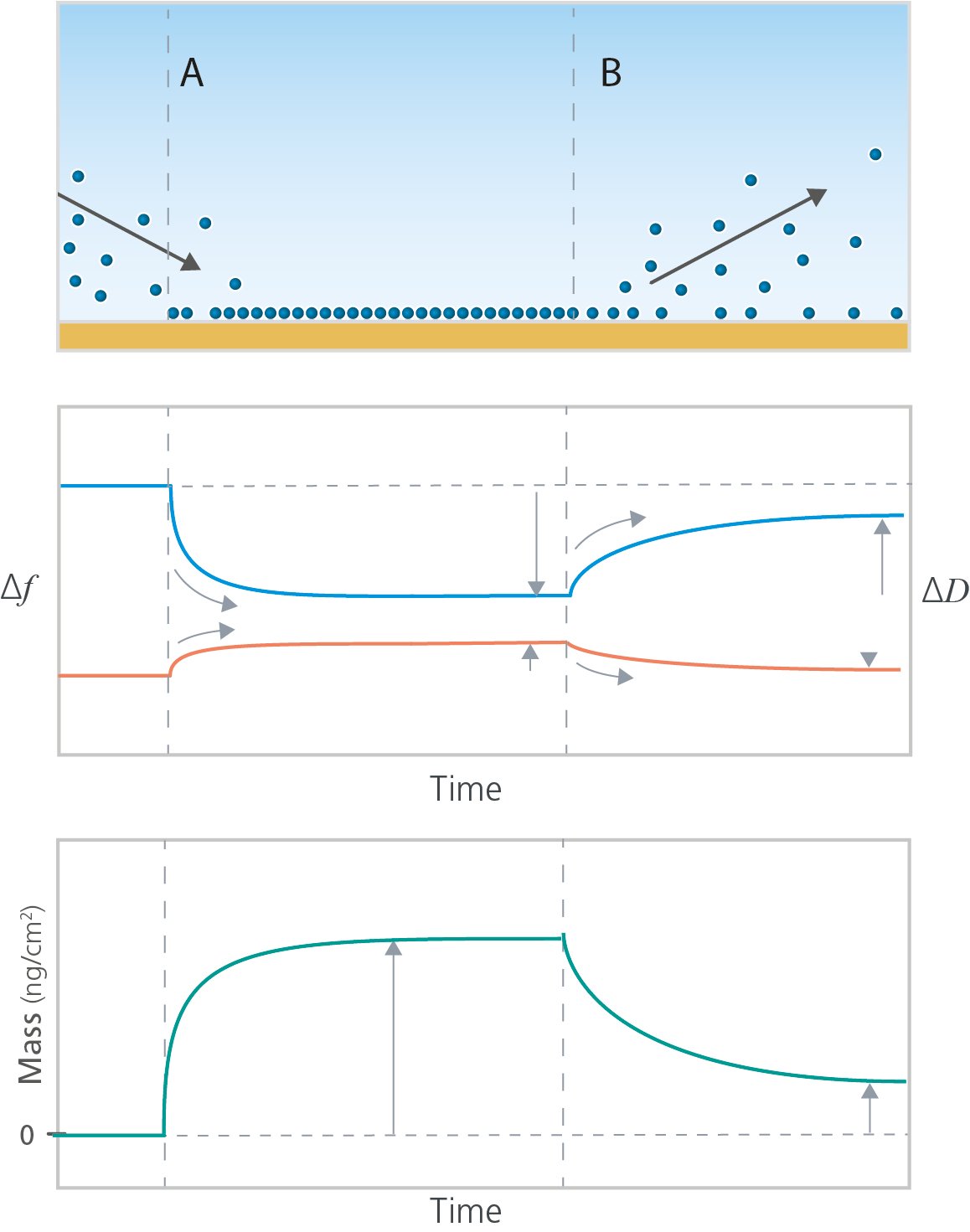
Figure 1. Schematic illustration (top panel) of (A) adsorption and (B) desorption of biomolecules to a surface, characterized by QSense QCM-D (middle panel). The Δf and ΔD data reflect mass change and layer softness respectively. As indicated by the grey arrows in the schematic graphs, the time-resolved data makes it possible to follow the adsorption and desorption, how fast they are, how much material that is added to and lost from the surface. The amount adsorbed to, and desorbed from, the surface can also be analyzed via quantification of the time-resolved layer mass (bottom panel) or layer thickness (not shown)
In addition to sensing changes of mass at the surface, QCM-D also senses the mechanical properties of the surface-adhering layer. This makes it possible to analyze the arrangement of the adsorbed biomolecules. For example, is the molecular layer densely or loosely packed? Are the molecules taking a collapsed conformation or do they stretch out from the surface? And is the packing arrangement the same throughout the entire adsorption process, or does it depend for example on surface coverage or any other parameter such as surface material, temperature, salt concentration, or pH?
There are many situations where biomolecular interaction with, and adsorption to, solid surfaces have an important role to play. For example, when designing biomaterials, in tissue engineering, in developing biosensors, and when assessing the interaction between a pharmaceutical drug and storage containers, bags and syringe materials. One tool that can be used to characterize such biomolecular adsorption is QSense QCM-D
QSense QCM-D can, for example, be used to:
Learn how QSense QCM-D reveals protein–surface interactions and adds interface-focused insight to biopharmaceutical formulation and stability work
Learn how QSense sensors enable application‑relevant biointerface interaction analysis and explore our sensor offering for different areas
Learn how QSense QCM D can be used to analyze swelling of thin films, including magnitude and dynamics.
Read about how molecule-surface interaction processes such as adsorption and desorption can be analyzed with QCM-D.
Learn best practices and step-by-step methods for accurate QCM-D coating thickness measurement on QSense sensors using QSense Omni.
Compared to QCM, QCM-D measures an additional parameter, and provides more information about the system under study.
Discover how QCM-D analysis reveals real-time etching dynamics, helping optimize cleaning processes and protect surfaces from unwanted damage.
Discover how QSense QCM-D helps tackle fouling challenges across industries
Discover how QCM-D enables real-time, label-free analysis of supported lipid membrane formation, structure, and dynamics for advanced research
