
Contamination control and surface cleanliness is key for successful silicone processing. Here we show how QSense technology can be used to analyze contaminant adsorption and desorption at various conditions, and to assess and compare the efficiency of post CMP cleaners
QSense technology is based on Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring, QCM-D, which is a surface sensitive real-time technology for analysis of molecule-surface interactions and layer properties at the nanoscale. Monitoring changes in resonance frequency, f, and dissipation, D, of a quartz crystal, surface interactions and layer properties can be characterized and quantified in terms of mass, thickness, and viscoelastic properties.
The information provided by QSense QCM-D allows for analysis of, for example, molecular adsorption/desorption, surface etching, and cleaning processes.
In the context of cleaning analysis, the method is suitable to:
The technology is also used in more fundamental work. For example, in a study1 by Wu et al., QSense QCM-D was used to investigate the fundamentals of contaminant adsorption and desorption to gain insights that would help develop chemistries and processes suitable for the 10 nm technology node and beyond.
The model system used in this study was benzotriazole (BTA), a copper corrosion inhibitor used in barrier CMP slurries and post-CMP cleaning formulations, adsorbed on Copper. Then, tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) and acetohydroxamic acid (AHA) -based solutions were used to analyze the BTA removal.

As already mentioned, the cleaning efficiency is analyzed by looking at the mass loss from the sensor surface, i.e., the mass removal rate and total amount removed. To run such an analysis, the key steps in the measurement is to first add the chemical or component, which is later to be removed by the cleaning agent, to the surface. Fig. 1. Next, the surface adhering layer is exposed to the cleaning agent of interest and the mass removal is monitored.
In this example, we would like to analyze and compare the removal efficiency of slurry additive using two different cleaning agents. We would like to compare the removal rates and the total amount removed. We run two experiments using the same surface chemistry and solvent conditions in the two cases, Fig 1.
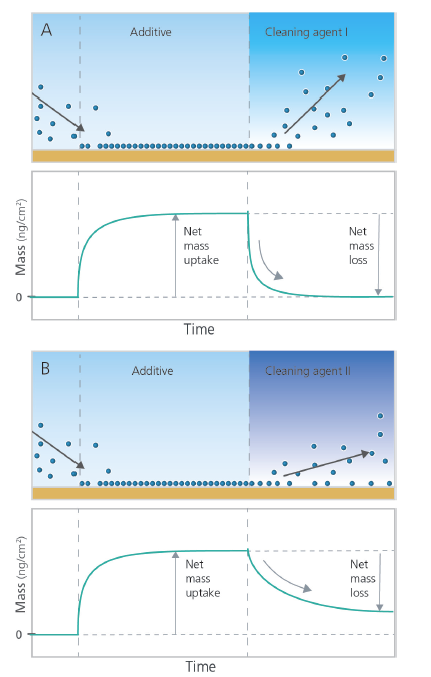
Figure 1. Schematic illustration (not to scale) of how post CMP cleaning and residue removal can be analyzed and compared using QSense QCM-D.
QSense technology provides time-resolved information on surface-molecule interactions which can be used to analyze and compare the efficiency of post-CMP cleaning approaches, and to explore how to best remove post-CMP residue.
Download the overview to learn more about QSense analysis in CMP
Learn how QSense QCM-D reveals protein–surface interactions and adds interface-focused insight to biopharmaceutical formulation and stability work
Learn how QSense sensors enable application‑relevant biointerface interaction analysis and explore our sensor offering for different areas
Learn how QSense QCM D can be used to analyze swelling of thin films, including magnitude and dynamics.
Read about how molecule-surface interaction processes such as adsorption and desorption can be analyzed with QCM-D.
Learn best practices and step-by-step methods for accurate QCM-D coating thickness measurement on QSense sensors using QSense Omni.
Compared to QCM, QCM-D measures an additional parameter, and provides more information about the system under study.
Discover how QCM-D analysis reveals real-time etching dynamics, helping optimize cleaning processes and protect surfaces from unwanted damage.
Discover how QSense QCM-D helps tackle fouling challenges across industries
Discover how QCM-D enables real-time, label-free analysis of supported lipid membrane formation, structure, and dynamics for advanced research
