Good adhesion is generally required whenever a coating is applied to a surface. In addition to a common case of painting, for example, adhesion is important in many industrial processes as well. Many products are composed of layers of different materials that all have specific function in a final product. For example, a milk carton is composed of layers of paper and polymer films and electronic sensor is a complex device with altering conductive and insulation layers. In order to these products fulfill their function, good adhesion between different layers is required. So, what are the requirements for good adhesion?
The most common reasons for adhesion failure are contamination. Any type of grease, oil or other impurities on the surface can cause the loss of adhesion. Making sure that the cleaning protocols are in place in your process is one of the most important things to ensure successful manufacturing. One way to determine the cleanliness of the surface is through contact angle measurements. As the contamination is often non-polar by nature, the contact angle of water on the unclean surface is higher than on a clean surface.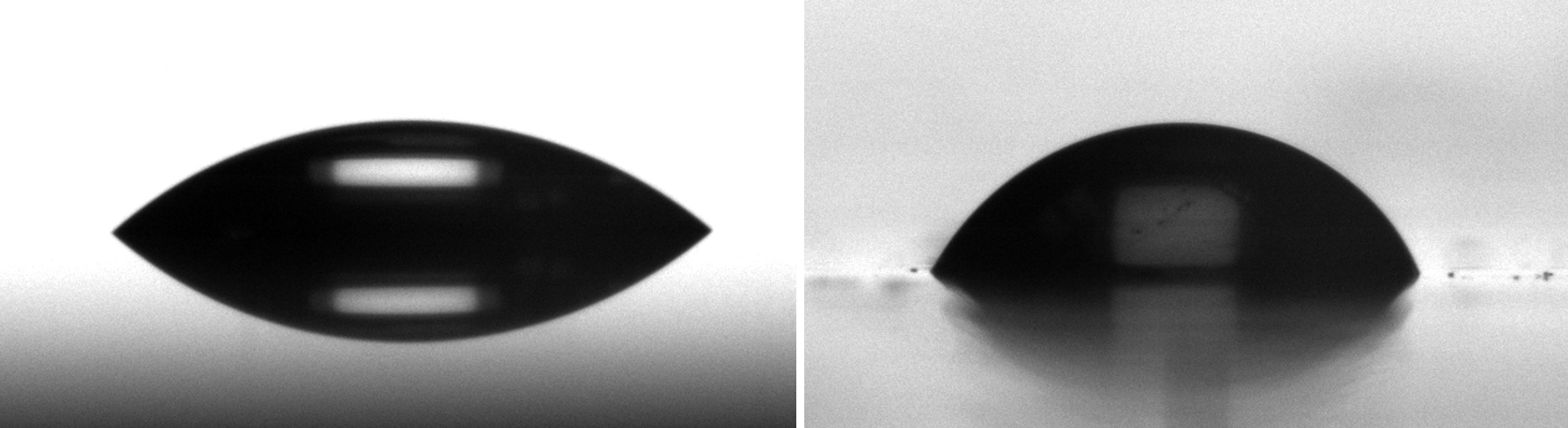
Drop of water on (left) Clean glass surface (right) dirty glass surface
Apart from cleaning the surface, some type of surface treatment may also be required to ensure good bonding between the two layers. One of the most used surface treatments is plasma treatment. In addition to providing an extra cleaning step for the surface, it will also improve the wettability of the substrate through the introduction of hydroxyl-, carboxyl and/or amine groups. Good surface wettability is prerequisite to good adhesion.
Water contact angle measurements can again be used to evaluate the impact of selected surface treatment method. To read more how contact angle measurements have been utilized in industrial processes, please download the review below.
Learn how to use contact angle measurements to evaluate surface cleanliness on different materials and link cleaning steps to reliable adhesion and coating quality.
Standard contact angle measurement considers the surface's chemical properties. The influence of surface roughness is added by utilizing the Wenzel equation.
Cohesion and adhesion are fundamental concepts in the study of physics and chemistry, playing crucial roles in various natural and industrial processes.
Surface inspection is done to guarantee optimum surface properties for coating and bonding
A spreading coefficient is a measure of the wetting behavior of a liquid on a solid surface.
Wetting and adhesion analysis has been added to our all-inclusive OneAttension software and is available for download for all OneAttension customers.
Depending on the strength of these forces, the adhesion failure can be either adhesive, cohesive, or substrate failure.
One of the main challenges in PCB manufacturing is the adhesion of the conformal coating. Contact angle measurements can be used to predict adhesion.
Adhesion problems are one of the main reasons for the failure of the product. Read to find out how contact angle measurements can help solve the problem.
