
Adhesive bonding is a process where two similar or dissimilar materials are fastened together. As the name implies, in adhesive bonding, an adhesive, typically some kind of glue is used to bond the two surfaces. In the adhesive bonding process, both adhesive and cohesive forces are involved. Depending on the strength of these forces, the adhesion failure can be either adhesive, cohesive, or substrate failure.
When the glue is applied on the surface, its ability to wet the surface is of utmost importance for good adhesion. Good wettability ensures that the glue can penetrate surface structures which leads to better mechanical interlocking at the interface. The adhesive forces between the glue and the substrate as well as the cohesive forces in the glue determine how well the glue can wet the surface. If the cohesive forces inside the glue (or any other coating formulation for that matter) are high, the glue prefers to stay together rather than interact with the surface. However, if the adhesive interaction between the substrate and the glue is high enough, the glue might spread after all. Once the glue has hardened and the interfaces are formed, these same forces determine whether the bonding is permanent or adhesion failure is likely to happen.
To understand why bonding fails, we need to first define the ways the failure can occur. 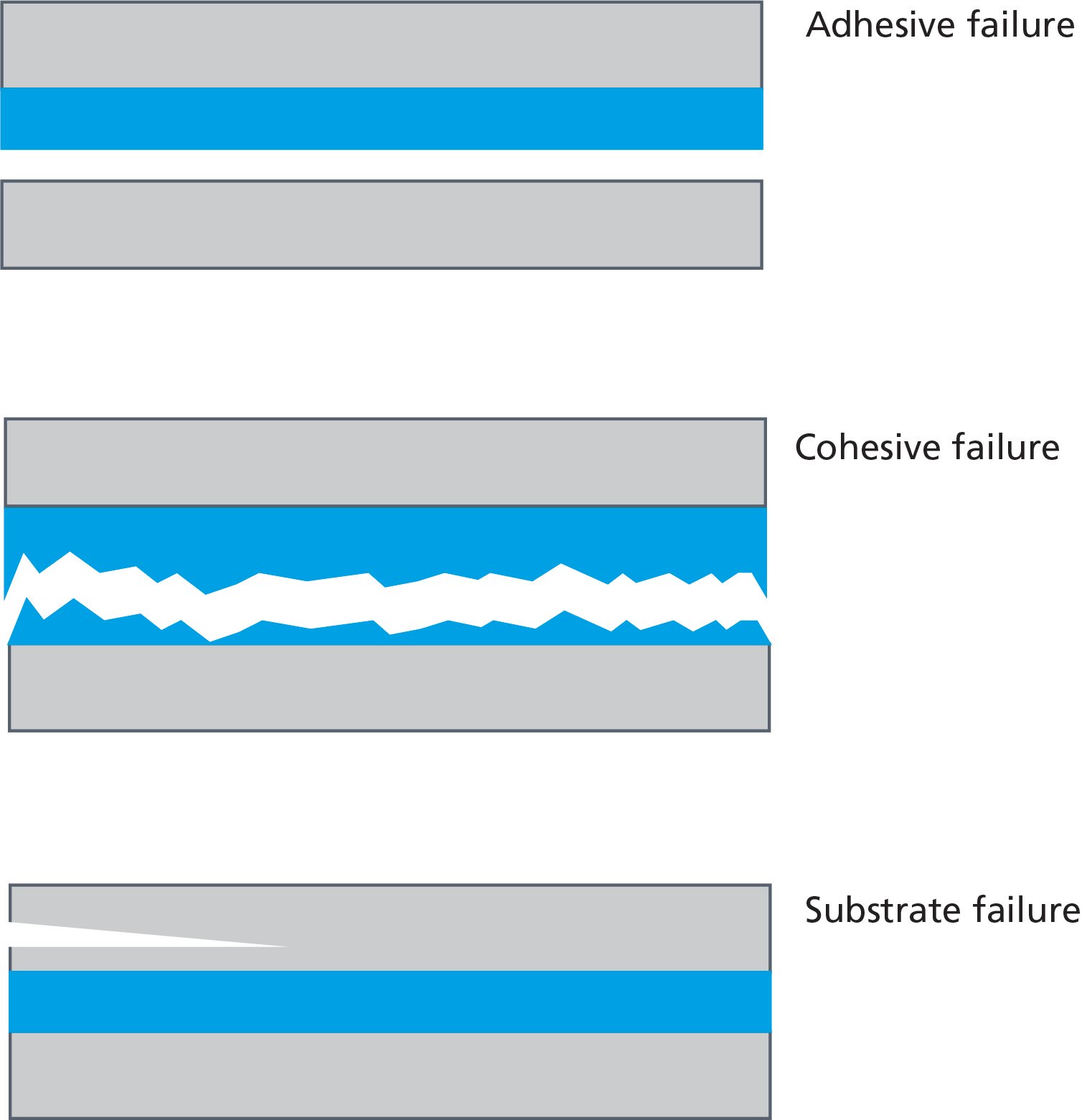 These can be divided into three categories:
These can be divided into three categories:
Adhesive failure, or delamination, is one of the most common types of failure mechanisms. There the two dissimilar materials detach from each other. The failure can happen between the adhesive and either of the two substrates, it is bonding together. Cohesive failure happens in the adhesive itself or inside the layer of a coating. Substrate failure is not related to the bonding process itself as it is a problem in a substrate.
As you might guess already, the cohesive failure will happen if the cohesive forces inside the adhesive are not strong enough. Then, on the other hand, the adhesive failure happens if the glue has not spread properly on the substrate. To make sure that the spreading of the glue (or other coating formulation) is sufficient, contact angle measurements can be used.
To read more about adhesion and how contact angle measurements can help to predict its success, please download the white paper through the link below.
Learn how to use contact angle measurements to evaluate surface cleanliness on different materials and link cleaning steps to reliable adhesion and coating quality.
Standard contact angle measurement considers the surface's chemical properties. The influence of surface roughness is added by utilizing the Wenzel equation.
Cohesion and adhesion are fundamental concepts in the study of physics and chemistry, playing crucial roles in various natural and industrial processes.
Surface inspection is done to guarantee optimum surface properties for coating and bonding
A spreading coefficient is a measure of the wetting behavior of a liquid on a solid surface.
Wetting and adhesion analysis has been added to our all-inclusive OneAttension software and is available for download for all OneAttension customers.
One of the main challenges in PCB manufacturing is the adhesion of the conformal coating. Contact angle measurements can be used to predict adhesion.
Adhesion problems are one of the main reasons for the failure of the product. Read to find out how contact angle measurements can help solve the problem.
